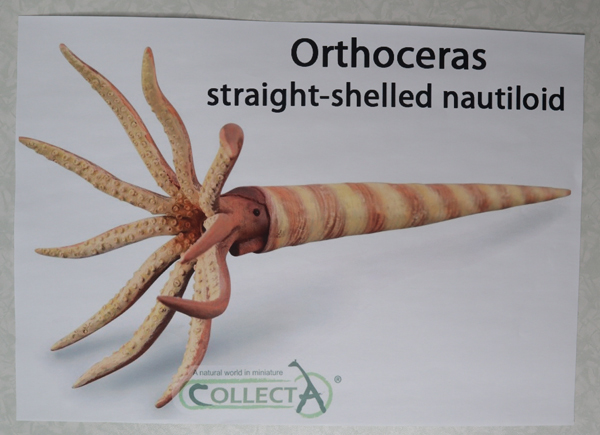
A Splendid Straight-shelled Nautiloid Pictured
The Silurian is a relatively short geological time period when compared to the other periods outlined in the geological time scale. The Silurian lasted around twenty-five million years (444 million years ago to approximately 419 million years ago). Although it was brief, in relative terms, during the Silurian the first land plants evolved and many invertebrate forms began to make the transition to a terrestrial habit. Life in the seas still dominated the Earth’s biota. One of the apex, marine predators was the straight-shelled nautiloid. Some of these orthocones evolved into giants.

Picture credit: Everything Dinosaur
Straight-shelled Nautiloid
During the Silurian most of the nautiloid cephalopods had straight or slightly curved shells. The planispiral forms had yet to become common. The last straight-shelled forms (Orthocerida), probably died out during the Mesozoic. Most straight-shelled nautiloids became extinct at the end of the Triassic, but one fossil specimen collected in the Caucasus (Zhuravlevia insperata), indicates that one species persisted into the Early Cretaceous.
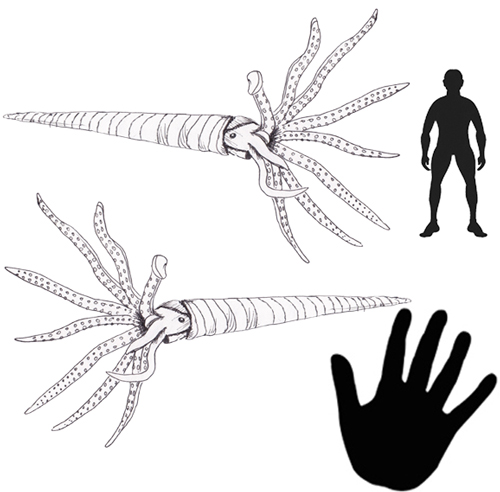
Picture credit: Everything Dinosaur
Zhuravlevia insperata
Described in 1994 by Larisa Doguzhaeva of the Swedish Museum of Natural History, based on a fragmentary orthocerid fossil, Zhuravlevia insperata is the geologically youngest straight-shelled orthocone known to science. The tiny fossil, just 1.3 cm long, with four chambers preserved, was found when Aptian-aged concretions from the Hokodz River Basin in the north-western Caucasus (Russia), were being split.
The orthocone fragment would be around 120 million years old.
CollectA introduced an Orthocone replica in 2020. The figure was added to the Age of Dinosaurs Popular range.
To view the invertebrate figures in the CollectA not-to-scale range including (whilst stocks last), Orthoceras: CollectA Age of Dinosaurs Popular Range.

