A student from the University of Bristol has confirmed the presence of Kuehneosaurs in the Late Triassic of southwestern England. These gliding reptiles were part of a rich reptile dominated fauna that lived on a series of sub-tropical islands, part of an ancient archipelago. The biggest island extended from Frome in the east to Weston-super-Mare in the west. It was around eighteen miles (thirty kilometres long). It is referred to as the Mendip Palaeo-island.
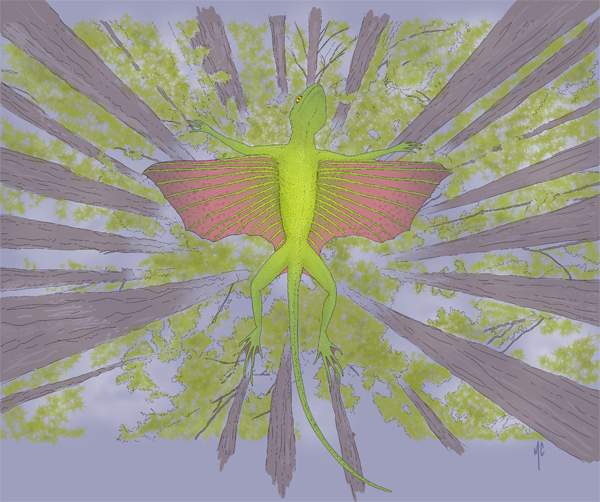
Picture credit: Mike Cawthorne
Kuehneosaurs on Sub-tropical Islands
Kuehneosaurs superficially resemble lizards. However, they were more closely related to the ancestors of crocodilians and dinosaurs. They were small animals, which could fit neatly on the palm of a hand, and there were two species present. One species had extensive wing flaps, the second species had much shorter wings. These wings consisted of skin stretched over elongated ribs. Powered flight was beyond them, but they probably were very competent gliders.
Kuehneosaurs probably occupied a niche in the ecosystem similar to the extant flying lizard Draco from southeast Asia. They most likely wandered about on the ground and climbed trees in search of insects and other small invertebrates. To escape from predators, or to make rapid progress through the trees, they could launch themselves into the air and glide for several metres.
The discovery of Kuehneosaurs in the Late Triassic ecosystem was made by University of Bristol Masters student Mike Cawthorne. He had been examining numerous reptile fossils collected from limestone quarries, which represent deposits associated with the Mendip Palaeo-island.
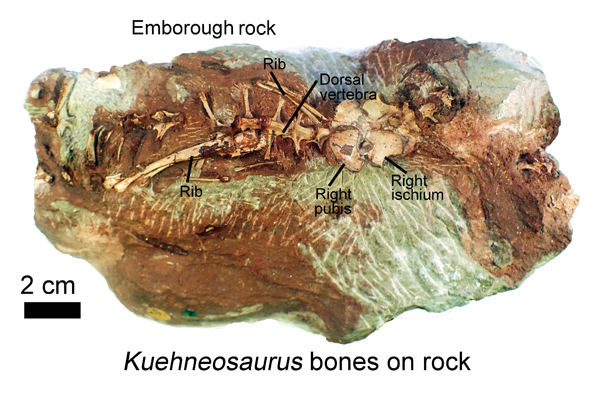
Picture credit: David Whiteside
No Dinosaur Fossils Found but They Were Probably Present
The research, published in the “Proceedings of the Geologists’ Association”, also records the presence of reptiles with complex teeth, the trilophosaur Variodens and the aquatic Pachystropheus that probably lived a bit like a modern-day otter likely eating shrimps and small fish. However, no dinosaur bones were found. These animals either fell or their bones were washed into caves and cracks in the limestone. This led to their preservation and the development of a fossil assemblage.
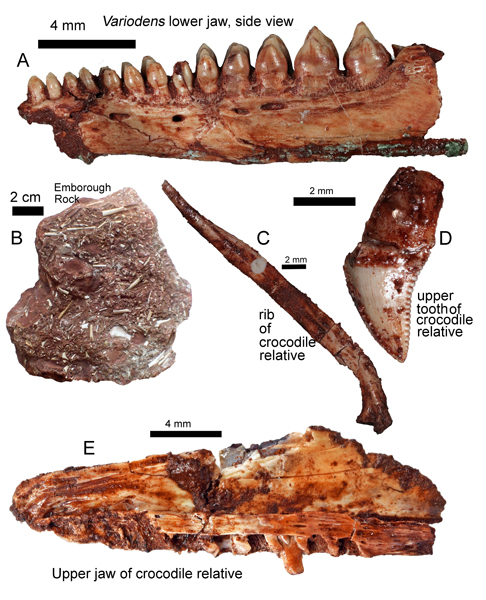
Picture credit: David Whiteside
Masters student Mike Cawthorne commented:
“All the beasts were small. I had hoped to find some dinosaur bones, or even their isolated teeth, but in fact I found everything else but dinosaurs. The collections I studied had been made in the 1940s and 1950s when the quarries were still active, and palaeontologists were able to visit and see fresh rock faces and speak to the quarrymen.”
A Home for a Diverse Assemblage of Small Reptiles including Kuehneosaurs
Professor Mike Benton from Bristol University’s School of Earth Sciences added:
“It took a lot of work identifying the fossil bones, most of which were separate and not in a skeleton. However, we have a lot of comparative material, and Mike Cawthorne was able to compare the isolated jaws and other bones with more complete specimens from the other sites around Bristol. He has shown that the Mendip Palaeo-island, which extended from Frome in the east to Weston-super-Mare in the west, nearly 30 km long, was home to diverse small reptiles feeding on the plants and insects. He didn’t find any dinosaur bones, but it’s likely that they were there because we have found dinosaur bones in other locations of the same geological age around Bristol.”
Paying Tribute to the Fossil Collectors
Dr David Whiteside (University of Bristol) praised the work of the amateur fossil collectors and academics who found the fossils stating:
“The bones were collected by some great fossil finders in the 1940s and 1950s including Tom Fry, an amateur collector working for Bristol University and who generally cycled to the quarries and returned laden with heavy bags of rocks. The other collectors were the gifted researchers Walter Kühne, a German who was imprisoned in Great Britain in the second world war, and Pamela L. Robinson from University College London. They gave their specimens to the Natural History Museum in London and the Geological collections of the University of Bristol.”
Everything Dinosaur acknowledges the assistance of a media release from the University of Bristol in the compilation of this article.
The scientific paper: “Latest Triassic terrestrial microvertebrate assemblages from caves on the Mendip palaeoisland, S.W. England, at Emborough, Batscombe and Highcroft Quarries” by M. Cawthorne, D. I. Whiteside, and M. J. Benton published in the Proceedings of the Geologists’ Association.
Visit the Everything Dinosaur website: The Everything Dinosaur Website.







Leave A Comment