Scientists have described the first dicraeosaurid sauropod dinosaur known from India. The dinosaur, named Tharosaurus indicus roamed northwestern India during the Middle Jurassic. At around 167 million years old, Tharosaurus indicus represents the earliest diplodocoid dinosaur described to date. It lived at least ten million years earlier than famous North American diplodocids such as Apatosaurus and Diplodocus, to which it was distantly related.
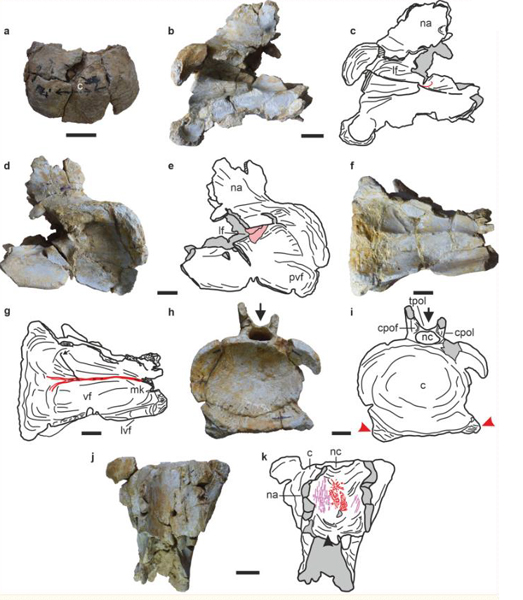
Fragmentary Fossils from Rajasthan
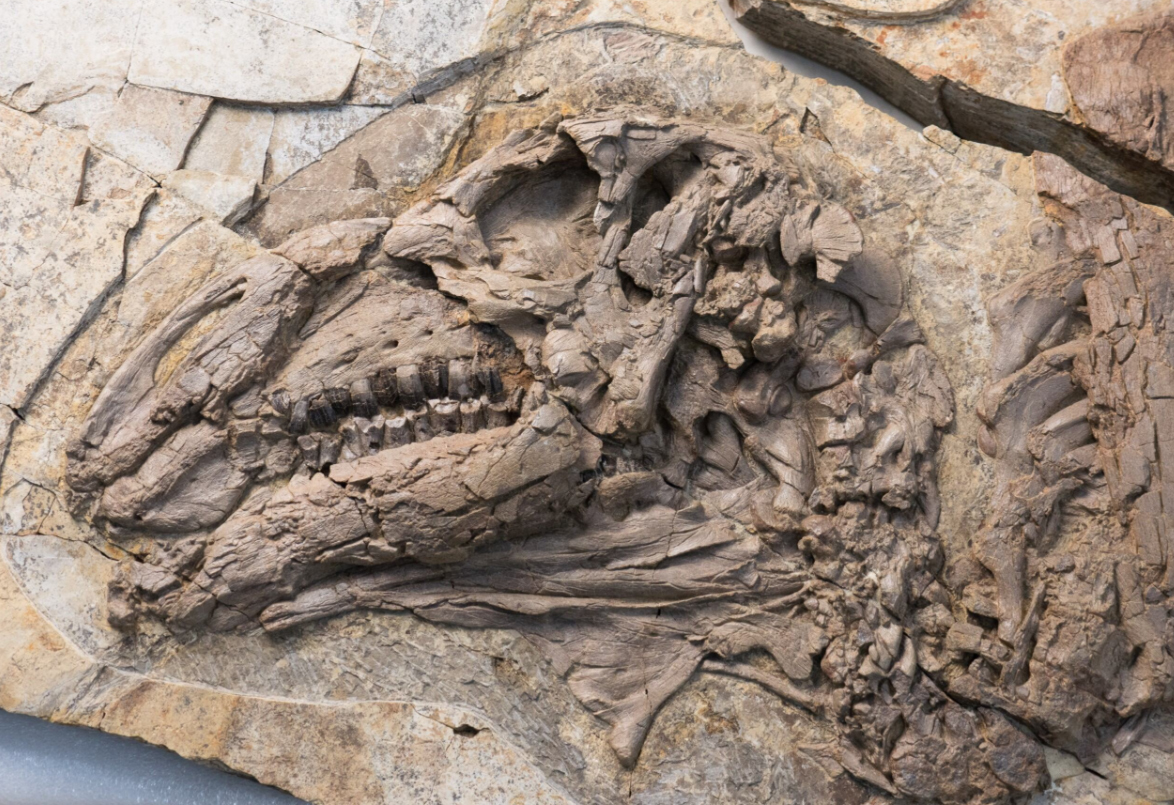
The fragmentary and disarticulated fossils consisting of vertebra and a solitary rib are believed to represent a single animal. The fossils were excavated from shale deposits just north of the village of Jethwai in Rajasthan State. The area is hot and arid, and it is known as the Great Indian Desert or the Thar Desert. The genus name of this new dinosaur references the Thar Desert, in recognition of the location of the fossil finds. The specific name honours the country of origin – India.
The fossil material was excavated from a bedding plane located at the base of the Fort Member (Jaisalmer Formation) with represents an early to middle Bathonian faunal stage deposition.
The Dicraeosauridae
The dicraeosaurids are a clade of small-bodied diplodocoid sauropods classified by their distinctive vertebrae with long paired neural spines. They are both temporally and geographically dispersed with fossils found in Africa, South America as well as China and the USA. The discovery of Tharosaurus extends their temporal range from the Bathonian faunal stage of the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous.
Picture credit: Everything Dinosaur
The dicraeosaurid illustration (above) is based on the Haolonggood Dicraeosaurus 1:35 scale replica.
To view the range of Haolonggood dinosaur models: Haolonggood Dinosaur Models.
New Insights into Sauropod Diversity
The research team suggest that Tharosaurus indicus is a relic of a sauropod lineage that originated in India and underwent rapid dispersal across the rest of Pangaea. Writing in the academic journal “Scientific Research”, the scientists conclude that this fossil discovery provides new insights into sauropod diversity. It also has important implications for the origin and dispersal of neosauropod dinosaurs.
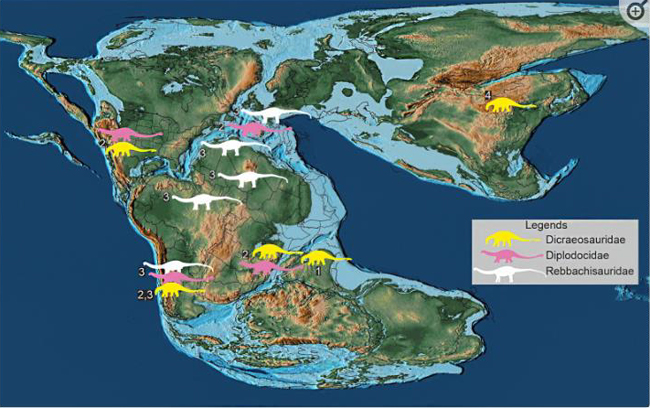
Tracing the Origins of the Sauropoda
The Sauropoda is thought to have originated in the Late Triassic/Early Jurassic. The origin and radiation of the Neosauropoda and its major clades (Macronaria and the Diplodocoidea) remains contentious. Non-neosauropods were restricted to eastern Gondwana (Zimbabwe and India) and parts of Laurasia (China, Germany and Thailand) during the Late Triassic/Early Jurassic. This suggests that there were barriers preventing their dispersal to the Americas and the most southerly portions of Gondwana. Although preservation and sampling biases cannot be ruled out, neosauropods possibly appeared during the late Early or early Middle Jurassic. The geologically youngest forms being associated with the Americas and Asia.
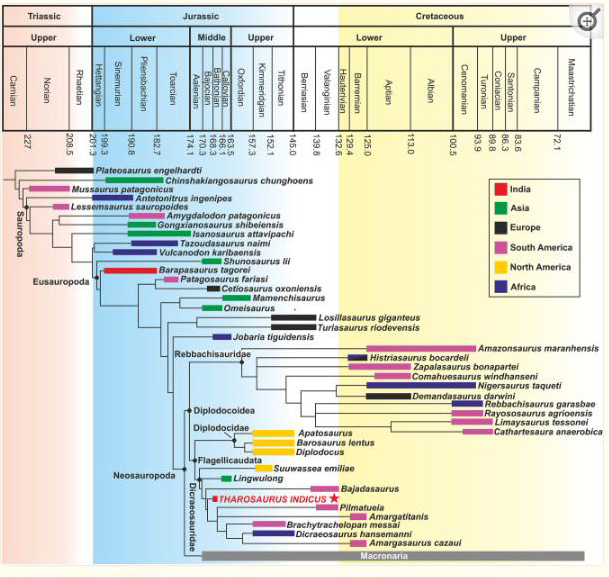
Tharosaurus indicus – Helping to Clarify Neosauropoda Evolution
Tharosaurus indicus is among the earlier-diverging dicraeosaurid dinosaurs, and its stratigraphic age (Bathonian) makes it the earliest known diplodocoid dinosaur globally. The authors of the paper stress the importance of the Lower and Middle Jurassic deposits of India and propose that further fossil discoveries will help to clarify the evolutionary history of the Neosauropoda.
The scientific paper: “Fossils of the oldest diplodocoid dinosaur suggest India was a major centre for neosauropod radiation” by Sunil Bajpai, Debajit Datta, Pragya Pandey, Triparna Ghosh, Krishna Kumar and Debasish Bhattacharya published in Scientific Reports.
Visit the award-winning Everything Dinosaur website: Everything Dinosaur.







Leave A Comment