Oxford University Museum of Natural History has completed the purchase of archive material belonging to pioneering geologist the Reverend William Buckland and his wife Mary (née Morland).
This is an important, historical and culturally significant archive that has been acquired by the Oxford University Museum of Natural History (OUMNH). The material which documents the contribution to science by the 19th century theologian and geologist contains over 1,000 items. There are notebooks, family papers, drawings, artworks and letters. The collection is noteworthy as it also highlights the contribution of Buckland’s wife Mary (née Morland). Mary was a talented artist and naturalist.

Funding the Acquisition
The acquisition has been made possible with support from the Friends of the National Libraries, Headley Trust, the Arts Council England/V&A Purchase Grant Fund and National Heritage Memorial Fund. Private donors also contributed.
Head of Earth Collections at the OUMNH, Eliza Howlett stated:
“The Museum’s acquisition of a large collection of Buckland papers from private hands is a game-changer for historians of science and others with an interest in the histories of gender, class, and colonialism. Combined with the already large and diverse Oxford collections, the new materials will confirm OUMNH as the epicentre for future research, and we are tremendously grateful to the many trusts and foundations, and to the private individuals, who generously contributed to this purchase.”
This important collection also includes correspondence between Mary Anning and William Buckland about new fossil discoveries. In a letter penned by Mary Anning the famous Lyme Regis resident informs the Reverend William Buckland about the discovery of Plesiosaurus remains.

William Buckland
William Buckland was a hugely influential figure in academia, religion, politics and science. He successively held the positions of Reader in Mineralogy and Geology at Oxford University; Dean of Westminster and Canon of Christ Church, Oxford.
He is accredited with the first, formal scientific description of a dinosaur (Megalosaurus bucklandii). This was one of three genera placed into the Dinosauria by Richard Owen in the early 1840s.

Picture credit: Everything Dinosaur
To view Megalosaurus models and replicas of other prehistoric creatures including dinosaurs: CollectA Prehistoric Life Figures.
The reverend William Buckland also pioneered palaeoecology with is ground-breaking study of an ancient hyena den. Buckland was also a notable convert to glacial theory, and showed how glaciation rather than a global flood shaped the British landscape.
An Insight into the Life of a Pioneering Scientist
This extensive archive reveals aspects of Buckland’s life as a student at Corpus Christi College, Oxford, as well his work as a practising geologist, eminent member of the clergy and university lecturer. Evidence from the archive provides a comprehensive insight into the thinking and institutions of the early 19th century. During this time, the biblical interpretation of creation was being challenged. Material in the archive documents correspondence with major figures such as art critic John Ruskin and prime minister Robert Peel.

Identifying Iconic Artworks
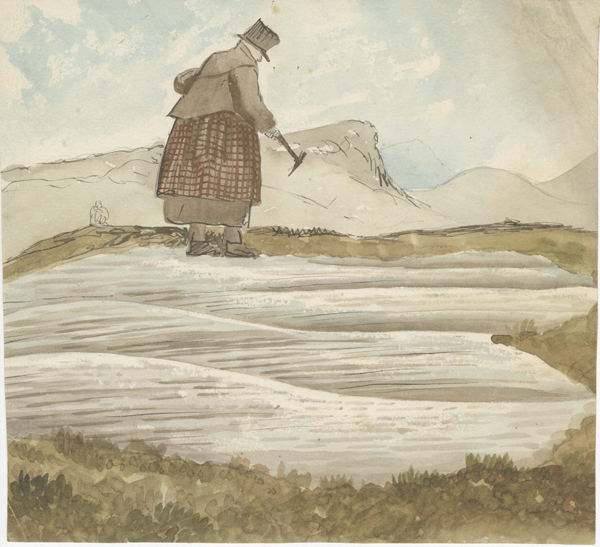
The archive also includes original artworks, such as Thomas Sopwith’s watercolour of William Buckland exploring a rock formation armed with a geological hammer. It had been thought that this artwork portrayed Mary Anning. The collection also includes an exceptionally rare, coloured version of the lithograph based on Henry de la Beche’s drawing Duria Antiquior. The artwork, depicting prehistoric Dorset, is famous for being the first pictorial representation of a scene of prehistoric life based on fossil evidence.
Mary’s Contribution is Recognised
This substantial archive also includes a number of illustrations created by Buckland’s wife Mary (née Morland). Highlights include two of Mary’s sketchbooks. One of these, dating from before her marriage to Buckland, contains exquisite ink and watercolour drawings of natural history specimens, and highlights the huge artistic and scientific contribution she made to her husband’s work.

Dr Simon Thurley CBE, Chair of the National Heritage Memorial Fund, commented:
“I am delighted the National Heritage Memorial Fund is able to support Oxford University Museum of Natural History to acquire the outstanding Buckland Archive and ensure that the collection remains together and is saved for the nation.”
Uniting the Collections
The Oxford University Museum of Natural History is already a significant repository for Buckland’s work. This new archive will fit with the Museum’s existing collection, helping to provide a more complete understanding of the contribution made to science and to scientific debate.
Reuniting these collections both physically and digitally will allow researchers and other museum audiences access to the full spectrum of Buckland material.
Everything Dinosaur acknowledges the assistance of a media release from the Oxford University Museum of Natural History in the compilation of this article.





Leave A Comment