Interbreeding between Early Modern Humans and Neanderthals
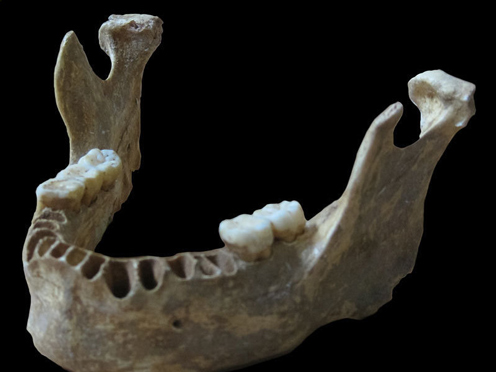
Scientists, including researchers from the Max Planck Institute of Evolutionary Anthropology (Leipzig, Germany), have analysed fragments of ancient human jawbone and discovered significant amounts of Neanderthal genetic material in the genome. The jawbone (mandible), comes from a cave complex in south-western Romania, the caves are famous for their mammal fossils and evidence of some of the earliest modern Europeans known.
The “Cave of Bones”
The cave is known as the “Peștera cu Oase”, this translates as the “cave of bones”, reflecting the abundance of prehistoric mammal bones associated with the cave.
Radiocarbon dating estimates that the jawbone is approximately 37,800 years old (37,000 to 42,000 years). The robust jaw and associated cranial material represent the oldest modern human (Homo sapiens) fossils known from Europe.
The Robust Human Jawbone Used in the Genetic Study
Picture credit: Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology/Svante Pääbo
Early Human Jawbone
In the genetic analysis, between six to nine percent of this individual’s genome originates from Homo neanderthalensis. Most modern humans (except sub-Saharan humans), have between one and three percent Neanderthal material in their genome. Scientists have suggested that interbreeding took place between these two closely related species between 50,000 and 60,000 years ago, but this new data suggests interbreeding in Europe took place much more recently.
The jawbone genetic material has a far greater concentration of Neanderthal genetic material than any other H. sapiens fossils or bones sequenced to date. As significant portions of this individual’s chromosomes are Neanderthal, it suggests that a Neanderthal was one of this person’s most recent ancestors, perhaps a great grandfather or a great grandmother.
For further information on this research: A Neanderthal in the Family?
Teaching Suggestions
Link to: Inheritance, Evolution and Variation (Key Stage 4 – Science/Key Stage 4 Evolution)
- The genome as the entire genetic material of an organism
- Evidence for evolution
- Genetic variation in populations of a species
- The process of natural selection leading to evolution
- How the genome and its interaction with the environment can influence the development of the phenotype of an organism
- Developments in biology affecting classification
Everything Dinosaur stocks a range of prehistoric human figures including Neanderthals and a model set that depicts the evolution of hominids.
The Evolution of Man Model Set
To view the range of prehistoric animal figures in stock at Everything Dinosaur: Safari Ltd. Evolution of Man Model Set/Prehistoric Figures.