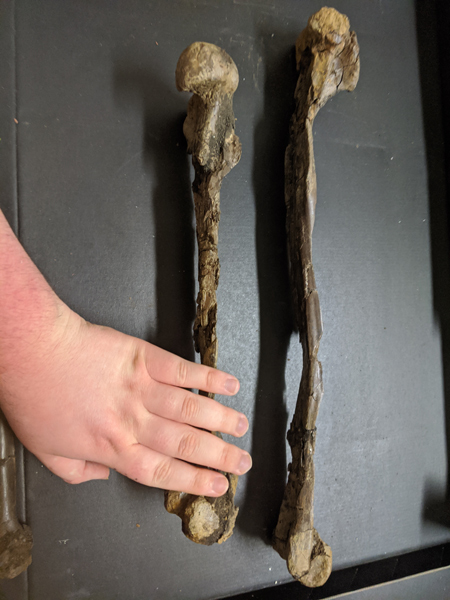
Getting to Grips with the Enigmatic Caenagnathidae
With the publication of the scientific paper announcing the discovery of Eoneophron infernalis, we at Everything Dinosaur thought we would take a closer look at the Caenagnathidae. The Caenagnathidae family (pronounced seen-nag-nay-thid-ay), are part of the Oviraptorosauria clade of maniraptoran theropod dinosaurs. They are closely related to the oviraptorids (Oviraptoridae family).
Picture credit: Everything Dinosaur
To read the recent article about Eoneophron infernalis: University Student Discovers New Dinosaur Species.
Defining the Maniraptora and the Oviraptorosauria
The Maniraptora clade consists of coelurosaurian dinosaurs and is defined as including the birds and the non-avian dinosaurs more closely related to them than to Ornithomimus velox. As well as containing the Oviraptorosauria, this clade also includes several other groups such as the dromaeosaurids, the Troodontidae family and the therizinosaurs.
The Oviraptorosauria clade* is comprised of the Caudipteridae family and two closely related dinosaur families the Caenagnathidae and the Oviraptoridae that together are classified as the Caenagnathoidea. The Oviraptorosauria are united by having very bird-like skeletons, with highly pneumatised bones. In addition, the rostrum is very short, and these dinosaurs have beaks. The beak is often, but not always edentulous (no teeth). These dinosaurs were all probably feathered.
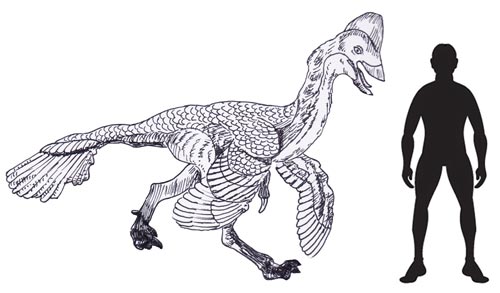
The image (above) depicts an Oviraptor model from the CollectA Age of Dinosaurs range.
To view this range of prehistoric animal figures: CollectA Age of Dinosaurs/Prehistoric Life Models.
The Caenagnathidae Family and Eoneophron infernalis
The family Caenagnathidae, together with its closely related sister family the Oviraptoridae, comprises the superfamily Caenagnathoidea. Virtually all known members of this superfamily are confined to the Late Cretaceous. Taxonomically the Caenagnathidae is defined as Chirostenotes pergracilis and all other theropods more closely related to it than they are to Oviraptor philoceratops.
Most of these dinosaurs tend to be quite small. As a result, they are probably underrepresented in the fossil record. For example, Anzu wyliei was thought until recently to be the only caenagnathid from the Hell Creek Formation. However, there are probably at least three caenagnathids present in Hell Creek strata, including the recently named Eoneophron infernalis.
Caenagnathids Not Closely Related to Ostriches
The Caenagnathidae family was originally erected by Raymond Martin Sternberg (1940), the son of the pioneering palaeontologist Charles Mortram Sternberg. Raymond Martin Sternberg thought that these dinosaurs were flightless birds. He erected the Caenagnathidae family which translates as “recent jaws”. It was mistakenly thought that these theropods were closely related to the Palaeognathae “old jaws” bird family. Extant palaeognath birds include the flightless Kiwi, the Ostrich and the Rhea as well as volant forms such as Tinamou birds. It is now known that the Caenagnathidae family of non-avian dinosaurs are not closely related to palaeognaths.
Caenagnathids are confined to the Late Cretaceous of Asia and North America. They tend to have small heads, long necks and short tails.
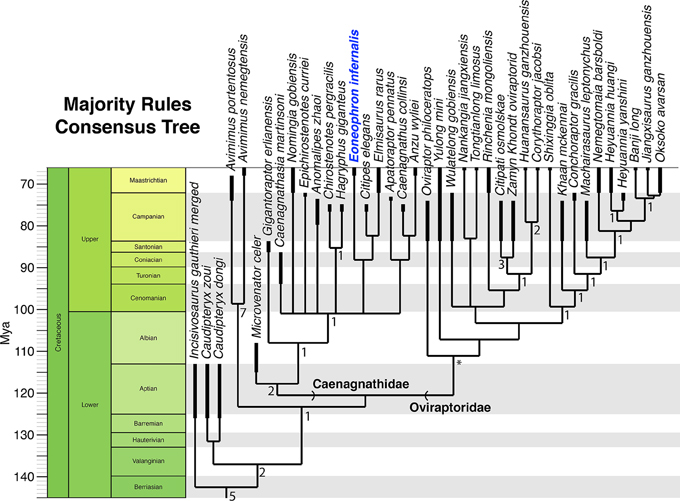
Challenging Phylogenetic Assessment
Whilst the fragmentary nature of most caenagnathid specimens makes phylogenetic assessment challenging, in the recent Eoneophron infernalis paper the researchers undertook a time-calibrated phylogenetic analysis of the Oviraptorosauria. Eoneophron was placed as a sister taxon to Citipes elegans and Elmisaurus rarus.
The difficulties involved in classifying oviraptorosaurs is exemplified by this placement. Although skeletal similarities between these three dinosaurs exist, there is a lack of comparable fossil material to study. Citipes elegans is geologically older. Its fossils come from the Dinosaur Provincial Park Formation of Alberta (Campanian faunal stage of the Late Cretaceous). In contrast, Elmisaurus rarus probably predates Eoneophron infernalis by a couple of million years. It too is from the Maastrichtian faunal stage of the Cretaceous. However, E. rarus fossils come from the Nemegt Formation of Mongolia.
A revision of already described specimens coupled with improved fossil sampling should help palaeontologists to gain a better understanding of the taxonomy of the Oviraptorosauria and specifically the enigmatic Caenagnathidae.
The Oviraptorosauria clade* also includes some other theropods regarded as basal members of this clade. For example, Incisivosaurus gauthieri from the Early Cretaceous of China.
Visit the Everything Dinosaur website: Everything Dinosaur.