Spinosaurus Not an Aquatic Dinosaur According to New Research
A recently published scientific paper has refuted the idea that Spinosaurus (S. aegyptiacus) was an aquatic dinosaur. Writing in the academic journal eLife, the researchers which included Paul Sereno (University of Chicago), conclude that Spinosaurus was not aquatic. Instead, they revert to the earlier hypothesis that this super-sized carnivore was a semi-aquatic, bipedal predator that did feed on fish but ranged far inland.
Over a decade ago, Everything Dinosaur team members were contacted by members of the CGI team working on the Spinosaurus segment of the soon to be launched television series entitled “Planet Dinosaur”. At the time, (2010), S. aegyptiacus was thought to be a semi-aquatic, bipedal predator that specialised in hunting fish, but was not thought to be an almost entirely aquatic dinosaur.

Picture credit: BBC Worldwide
The 2014 Scientific Paper
In 2014, Paul Sereno (the lead author of the latest paper), was one of the authors of a study into Spinosaurus material found in Morocco. In the paper, the researchers proposed that this huge theropod possessed adaptations that indicated a semi-aquatic lifestyle. The skull had small nostrils located further up the snout to allow this dinosaur to breathe whilst its jaws were partially submerged and neurovascular openings along the jaws were interpreted to be sense organs that permitted Spinosaurus to sense the movements of fish through the water. Analysis of the centre of gravity indicated that Spinosaurus was a quadruped.
To read Everything Dinosaur’s blog post about the 2014 study: Spinosaurus – Four Legs are Better than Two!
However, commenting on the 2014 paper, Professor Sereno admits that there was a mistake made when examining the centre of gravity of Spinosaurus. When the centre of gravity was calculated leading to the conclusion that this huge theropod walked on all fours, the volume of the lungs were not properly accounted for. When a new assessment of the centre of gravity is made, using a more accurate lung volume assessment, the results are radically different. The data suggests that Spinosaurus was a biped, with a typical posture associated with other large-bodied carnivorous dinosaurs.

The image (above) depicts Spinosaurus with the typical bipedal posture of a large-bodied theropod dinosaur. The model is a Nanmu Studio Spinosaurus (version 2.0).
To view the range of Nanmu Studio models and figures available from Everything Dinosaur: Nanmu Studio Dinosaur and Prehistoric Animal Replicas.
The Fleshy Spinosaurus Tail
In 2020, another paper was published which examined the caudal vertebrae of Spinosaurus aegyptiacus, tail bones having not been part of previous studies. Writing in the journal “Nature” the researchers which included Nizar Ibrahim (University of Detroit Mercy, Detroit), along with colleagues from the University of Portsmouth, proposed that Spinosaurus had a broad, flexible, fin-like tail that could have propelled this dinosaur through the water. This seemed to be the decisive evidence, that Spinosaurus was indeed an aquatic hunter.
To read Everything Dinosaur’s blog post about the 2020 paper: Spinosaurus – The River Monster.
Spinosaurus was not Aquatic
In this newly published research, Sereno and his colleagues looked at the biomechanics of the fin-like tail and analysed its effectiveness as an organ of propulsion through water. When compared to alligators, the tail and hind feet of Spinosaurus were found to be very inefficient swimming organs. Spinosaurus was an unstable, slow-surface swimmer only capable of a swimming speed of less than one metre a second.
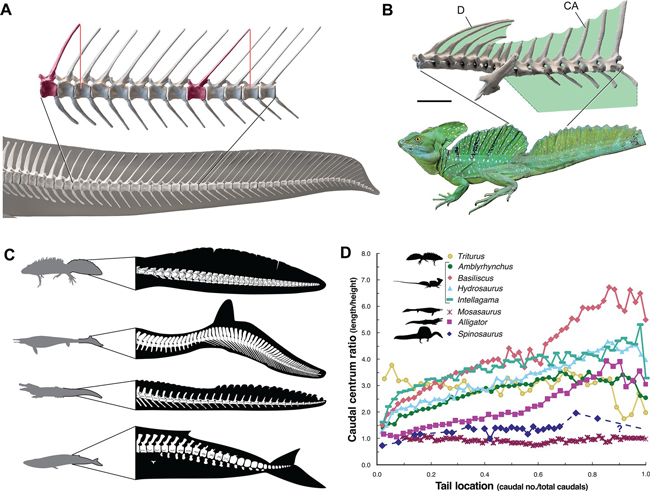
The team also calculated that Spinosaurus would have been too buoyant to submerge fully. It was not capable of diving and those robust, heavy hind limbs helped it to walk on land or wade, not acting as additional ballast to help this fifteen-metre-long giant remain underwater.
Sereno and his fellow authors suggest that living reptiles with similar tail bone morphology, such as the basilisk lizard, do not use their tails for propulsion, instead they have a display function.
Spinosaurus Ranged Far Inland
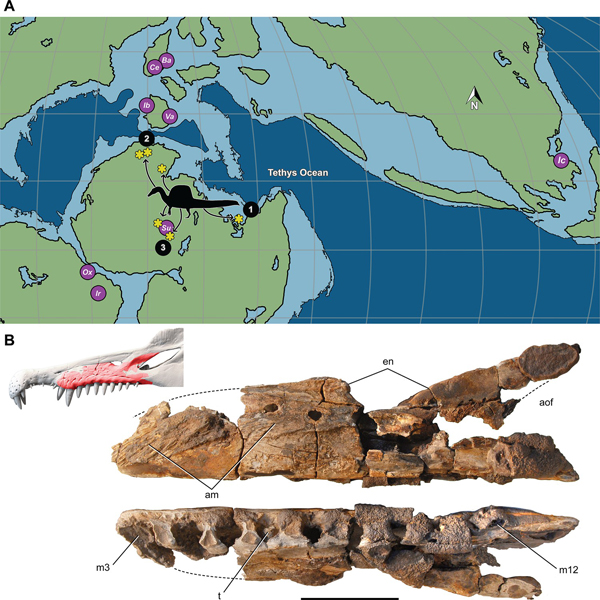
Fossils ascribed to Spinosaurus recovered from fluvial deposits in Niger suggest that this dinosaur ranged far inland. It is true that most Spinosaurus fossils come from sediments that represent extensive coastal deltas. However, these deposits include a large number of non-spinosaurid dinosaur remains, all of which may have been transported for some distance downstream. Spinosaurus fossil material may have also been transported, leading to the misconception that this was a dinosaur confined to the coast. Recently discovered fossils ascribed to Spinosaurus from two inland basins in Niger (Égaro North), indicate that Spinosaurus lived far from the shore. These fossils which include part of an upper jaw (maxilla) were found in fluvial deposits in association with rebbachisaurid and titanosaurian sauropods which are regarded as entirely terrestrial animals.
Comfortable in Water but Not Truly at Home in an Aquatic Environment
Confirming that the researchers think Spinosaurus was a bipedal, semi-aquatic animal that specialised in hunting fish, Professor Sereno added:
“Do I think this animal would have waded into water on a regular basis? Absolutely, but I do not think it was a good swimmer or capable of full submergence behaviour.”
Everything Dinosaur acknowledges the assistance of a media release from the University of Chicago in the compilation of this article.
The scientific paper: “Spinosaurus is not an aquatic dinosaur” by Paul C Sereno, Nathan Myhrvold, Donald M Henderson, Frank E Fish, Daniel Vidal, Stephanie L Baumgart, Tyler M Keillor, Kiersten K Formoso and Lauren L Conroy published in eLife.

