Nanjinganthus dendrostyla – Putting Back Flowering Plants by 50 Million Years
When did flowering plants (angiosperms) evolve? That has been a puzzling question, one that has taxed the minds of leading scientists for more than 200 years. Genetic studies indicate that the diverse and widespread angiosperms have an ancient lineage, but the fossil record does not support this idea. Fossils of delicate flowers are very rare and the oldest known, date from the Early Cretaceous. Time for the fossil record to catch up with the announcement of the discovery of a plant that produced flowers some 174 million years ago, during the late Early Jurassic (Toarcian stage).
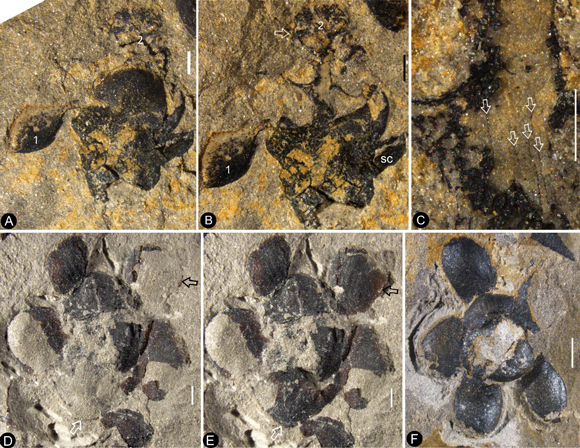
Specimens of the Newly Described Early Jurassic Flowering Plant Nanjinganthus dendrostyla
Picture credit: (NIGPAS)
The newly described plant has been named Nanjinganthus dendrostyla and it comes from the South Xiangshan Formation (Nanjing, eastern China), which has been studied extensively since the turn of the century and is famous for its abundant plant fossils, which up until now had consisted of cycads, ferns, ginkgoes and horsetails. Researchers from the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIGPAS), have been able to identify the earliest known examples of a flowering plant, one that predates most of the angiosperm fossil material by around 50 million years.
Fossils Catching Up with the Molecular Clock
Analysis of the genetic data contained in living plant taxa indicates that plants probably evolved earlier than previously thought. In a study published in February, researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences as well as Bristol University, mapped the genetic make-up of 644 types of plant and concluded, based on molecular dating, flowering plants (angiosperms), probably evolved sometime between the Late Permian and the Late Jurassic.
To read Everything Dinosaur’s article summarising this research: When Did Flowers Evolve?
Lots of Fossil Specimens to Study
The researchers studied a total of 264 specimens representing 198 individual flowers preserved on 34 slabs of stone. The scientists had the luxury of working on so many examples of the same fossil organism. They produced numerous high resolution images of the flowers allowing the features of N. dendrostyla to be revealed in great detail. With so many fossil specimens, the scientists were able to exclude other plant types and confirm that the fossils do indeed represent an angiosperm.
A Life Reconstruction of the Earliest Flowering Plant Described to Date
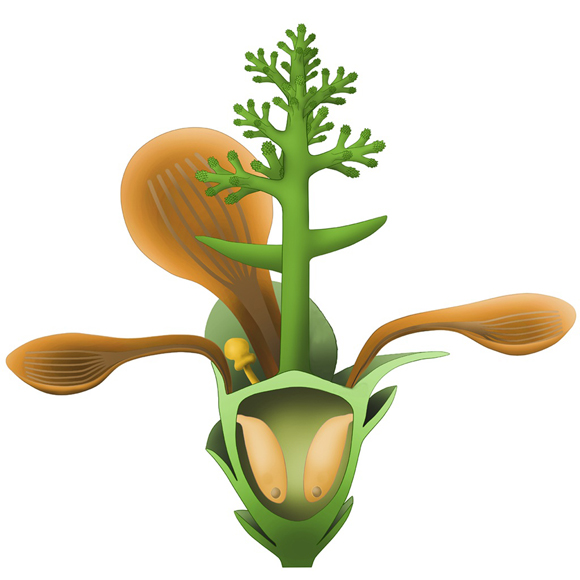

Picture credit: (NIGPAS)
Commenting on the significance of the study, one of the researchers Wang Xin (NIGPAS), stated:
“The origin of angiosperms has long been an academic headache for many botanists. Our discovery has moved the botany field forward and will allow a better understanding of angiosperms.”
Identifying a Key Feature of Angiosperms
The scientists were able to identify the presence of fully enclosed ovules in the fossilised flowers. These are the precursors of seeds before pollination. The reconstructed flower was found to have a cup-form receptacle and ovarian roof that together enclosed the ovules/seeds. This botanical feature confirms that Nanjinganthus dendrostyla is definitely an angiosperm.
Numerous Examples of N. dendrostyla Preserved in Siltstone
Picture credit: (NIGPAS)
Fossil Flowers in Jurassic Rocks
Discoveries of angiosperm-like fossils have been reported from Jurassic rocks before. In January (2018), Everything Dinosaur published an article on the remarkable discovery of fossilised wing scales from butterflies and moths that lived during the Late Triassic. This discovery challenged the theory of co-evolution between flowering plants and pollinating insects such as members of the Lepidoptera.
To read Everything Dinosaur’s article about this: Ancient Butterflies Flutter By.
The morphological features of Nanjinganthus distinguish it from other specimens and suggest that it is a new angiosperm genus.
The scientists hope to determine whether angiosperms are monophyletic (all flowering plants share a common ancestor). If this is the case and Nanjinganthus is one of the earliest of all the flowering plants, then these fossils represent a stem group giving rise to all later species. Angiosperms could also be polyphyletic, (a group descended from more than one common ancestor), meaning Nanjinganthus represents an evolutionary dead end and subsequently, it did not give rise to later types of flowering plant.
Visit the Everything Dinosaur website: Everything Dinosaur.







Leave A Comment